Honeybees: The Busy Life of Apis Mellifera, Nature's Vital Pollinators

Overview
In the vibrant tapestry of nature, honeybees, scientifically known as Apis mellifera, play an indispensable role as tireless pollinators. These extraordinary creatures, with their intricate social structure and remarkable work ethic, are responsible for nurturing the life cycle of countless plant species. Their contributions to ecosystems and agriculture are immeasurable, making them indispensable allies in preserving the delicate balance of our planet.
Unveiling the Honeybee's World
Honeybees inhabit a complex and fascinating world, characterized by a highly organized social hierarchy and unwavering dedication to the well-being of their colony. Within this bustling society, each individual bee fulfills a specific role, contributing to the hive's collective success.
4.9 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 44865 KB |
| Print length | : | 40 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |

The Queen: Matriarch of the Colony
At the helm of the honeybee colony sits the queen, the sole reproductively active female responsible for laying eggs and ensuring the continuity of the hive. She is the matriarch, attended to by a retinue of worker bees who tirelessly care for her needs and protect her from harm.
Worker Bees: The Hive's Unsung Heroes
The vast majority of honeybees within a colony are worker bees, sterile females who tirelessly perform a multitude of essential tasks to sustain the hive. These hardworking individuals can be further classified into various specialized groups, each responsible for distinct duties.
- Nurse Bees: Dedicated to nurturing the colony's young, nurse bees provide care and sustenance to the developing larvae.
- Forager Bees: Venture outside the hive to gather pollen and nectar, the lifeblood of the colony.
- Guard Bees: Vigilant protectors of the hive, guard bees stand watch at the entrance, defending against potential threats.
- Undertaker Bees: Responsible for maintaining the hive's hygiene, undertaker bees remove deceased bees and debris, ensuring the colony's health.
Drones: The Males of the Colony
Drones, the male honeybees, play a crucial yet limited role within the colony. Their primary responsibility lies in mating with the queen, ensuring the continuation of the species. Unlike worker bees, drones do not possess stingers and do not actively participate in the colony's daily tasks.
Honeybees as Nature's Pollinators
Honeybees' significance extends far beyond their fascinating social structure. As tireless pollinators, they play a vital role in maintaining the health and diversity of ecosystems worldwide. Their visits to flowers facilitate the transfer of pollen between plants, enabling fertilization and the production of seeds and fruits.
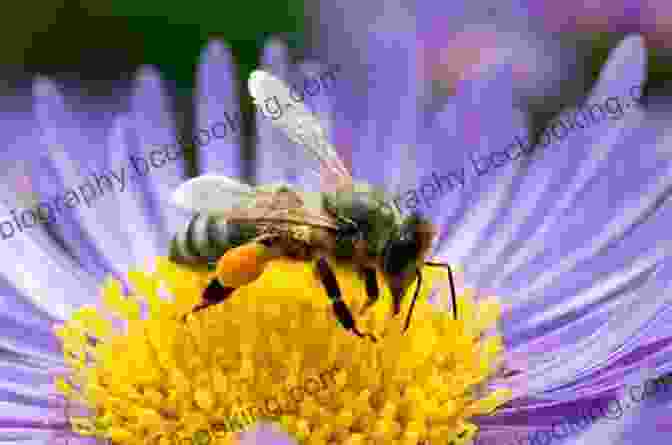

This intricate process of pollination is essential for the survival of countless plant species, including a wide variety of crops that sustain human life and various animal species. Without honeybees and other pollinators, the Earth's food supply would be severely compromised, and ecosystems would face drastic declines in biodiversity.
The Importance of Honeybees for Agriculture
Honeybees' pollination services are indispensable for modern agriculture. They are responsible for pollinating approximately one-third of the food we consume, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and oilseeds. Their contributions to the agricultural industry are staggering, resulting in billions of dollars in increased crop yields annually.
- Fruits: Apples, pears, peaches, strawberries, blueberries, and many more fruits rely on honeybees for pollination.
- Vegetables: Tomatoes, cucumbers, squash, peppers, and beans are just a few of the vegetables that benefit from honeybee pollination.
- Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, and pistachios are among the nut crops that depend on honeybees for pollination.
- Oilseeds: Canola, sunflower, and soybean are important oilseed crops that rely heavily on honeybee pollination.
Threats to Honeybee Populations
Despite their vital importance, honeybee populations are facing significant threats worldwide. Various factors, including pesticides, habitat loss, climate change, and parasites, are contributing to the decline of honeybee colonies.
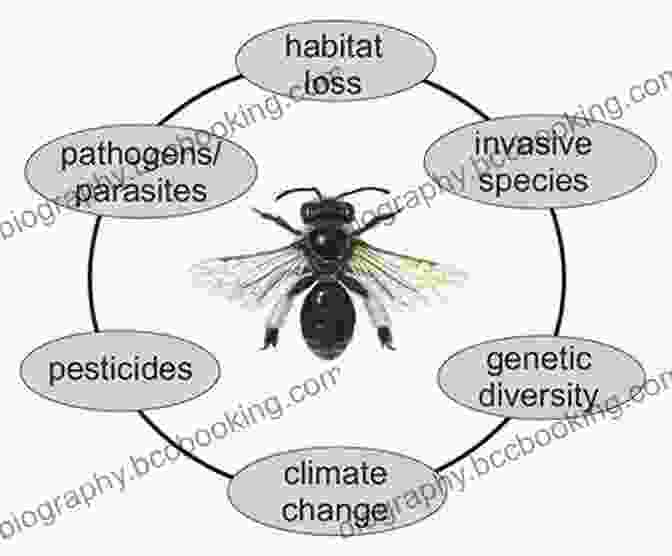
Recognizing the urgency of this issue, scientists, conservationists, and beekeepers are working diligently to implement measures to protect and restore honeybee populations. Educational campaigns, habitat restoration projects, and research into sustainable beekeeping practices are all part of the ongoing efforts to safeguard the future of these invaluable creatures.
Honeybees: A Call to Conservation
The survival of honeybees is inextricably linked to the health of our planet and the sustainability of our food systems. As responsible stewards of the environment, we have a collective responsibility to take action and protect these extraordinary pollinators.
- Reduce Pesticide Use: Limit the use of pesticides that are harmful to honeybees. Opt for organic or natural pest control methods whenever possible.
- Plant Bee-Friendly Flowers: Create a welcoming environment for honeybees by planting a variety of flowering plants that provide nectar and pollen throughout the year.
- Support Local Beekeepers: Encourage beekeeping practices that prioritize the well-being of honeybees and avoid the use of harmful chemicals.
- Educate Others: Spread awareness about the importance of honeybees and the threats they face. Encourage conservation efforts and inspire others to take action.
Honeybees, the tireless workers of the natural world, are essential pollinators that play a pivotal role in maintaining the health of ecosystems and ensuring the sustainability of our food supply. Their complex social structure, unwavering work ethic, and vital pollination services make them indispensable allies in the delicate balance of nature.
As we recognize the threats facing honeybee populations, it is imperative that we take immediate action to protect these invaluable creatures. By embracing conservation efforts, reducing pesticide use, planting bee-friendly flowers, supporting local beekeepers, and educating others, we can safeguard the future of honeybees and ensure their continued contributions to the well-being of our planet.
4.9 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 44865 KB |
| Print length | : | 40 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Cara J Stevens
Cara J Stevens Caroline Kepnes
Caroline Kepnes Candice Lau
Candice Lau Brian Pennell
Brian Pennell Carita Sundin
Carita Sundin Bruce Pascoe
Bruce Pascoe Bruce Lockwood
Bruce Lockwood Carolina Maria De Jesus
Carolina Maria De Jesus Cassandra Aarssen
Cassandra Aarssen Brian Jay Jones
Brian Jay Jones Carol Spencer Mitchell
Carol Spencer Mitchell Carrie Floyd Cagle
Carrie Floyd Cagle Candy Verney
Candy Verney Brian J Sorrells
Brian J Sorrells Carrie Ryan
Carrie Ryan Carole P Roman
Carole P Roman Brian Wood
Brian Wood Camila Hurst
Camila Hurst Camille Marawa
Camille Marawa Carrol L Henderson
Carrol L Henderson
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Leslie CarterTreasure Island Remix: Remixed Classics - A Literary Masterpiece Reimagined...
Leslie CarterTreasure Island Remix: Remixed Classics - A Literary Masterpiece Reimagined... Derrick HughesFollow ·2.4k
Derrick HughesFollow ·2.4k Clarence MitchellFollow ·11k
Clarence MitchellFollow ·11k Jason HayesFollow ·11.5k
Jason HayesFollow ·11.5k Jaime MitchellFollow ·15.1k
Jaime MitchellFollow ·15.1k Harvey HughesFollow ·14.8k
Harvey HughesFollow ·14.8k Arthur MasonFollow ·10.8k
Arthur MasonFollow ·10.8k Earl WilliamsFollow ·4.3k
Earl WilliamsFollow ·4.3k Howard PowellFollow ·3.5k
Howard PowellFollow ·3.5k

 Andy Hayes
Andy HayesUnveil the Rich Tapestry of Rural Life: Immerse Yourself...
Step into the enchanting pages of "Still...

 David Mitchell
David MitchellUnlocking the Depths of Cybersecurity: An In-Depth Look...
In the ever-evolving landscape of...

 Seth Hayes
Seth HayesUnlock the Secrets of Watercolor Landscapes: 37 Tools for...
Embark on a...
 Tyler Nelson
Tyler Nelson15 Insightful Answers to Questions on Uterine Fibroid
Uterine fibroids...

 Evan Hayes
Evan HayesAfrica In My Soul: A Literary Odyssey That Captivates the...
In a world where diverse cultures...
4.9 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 44865 KB |
| Print length | : | 40 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |